Difference No.1
Short Column: A column is considered to be short if the ratio of effective length to its least lateral dimension is less than or equal to 12. It’s buckling tendency is very low.
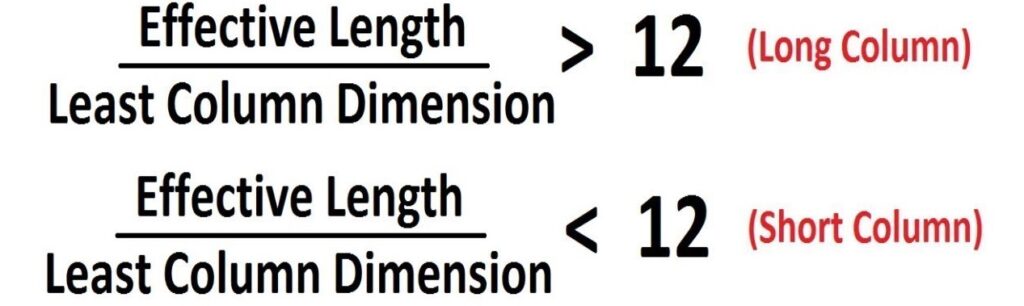
Long Column: A column is considered to be long if the ratio of effective length of column to its least lateral dimension is greater than 12.Longand slender columns buckle easily.
Example: 12”x20” Column effective length=11’6” Least dimension is here 12”=1ft. So Ratio=11.5ft/1ft=11.5<12 (Short Column)
For Circular column least dimension will be it’s diameter.
Difference No.2
Short Column: The ratio of effective length of a short column to its least radius of gyration (Slenderness Ratio) is less than or equal to 40.
Long Column: The ratio of effective length of a long column to its least radius of gyration(Slenderness Ratio) is greater than 40.
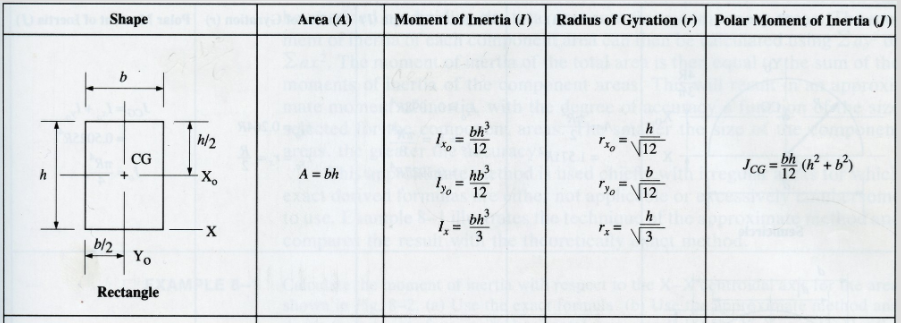
Example: Radius of gyration(K) is the distance from a given axis to the point where the entire area to be concentrated. K=Square root of (I/A). So if a 12”x20” Column having effective length=11’6”(138”) & least radius of gyration is 3.468”. So Slenderness Ratio=138/3.468=39.79<40 (Short Column)
A Bodybuilder Solved a Rubik’s Cube While Doing a Weighted Plank side effects of proviron ripped female bodybuilder fucks a vibrator in bedDifference No.3
Short Column: The load carrying capacity is high as compared to long column of the same cross sectional area.
Long Column: The load carrying capacity is less as compared to short column of the same cross sectional area.
Difference No.4
Short Column: The failure of the short column is by crushing.
Long Column: The column generally fails in buckling (Bending Failure).


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.